25 Commonly Confused Words in English

Words are the building blocks of our thoughts, ideas, and stories. However, the English language, with its rich history and diverse influences, can be complex, even for experienced writers. One challenge is commonly confused words, which are like linguistic doppelgangers that can trip up even the most careful writers.

To help you understand these confusing words, we'll explore 25 commonly confused words in English. We'll learn the subtle differences between them and how to avoid using them incorrectly.
First, remember this key to parts of speech for better understanding of the words.
Parts of speech key
n noun
v verb
adj adjective
prep preposition
pr pronoun
c contraction
conj conjunction
| Try Free Grammar checker.
Affect vs. Effect
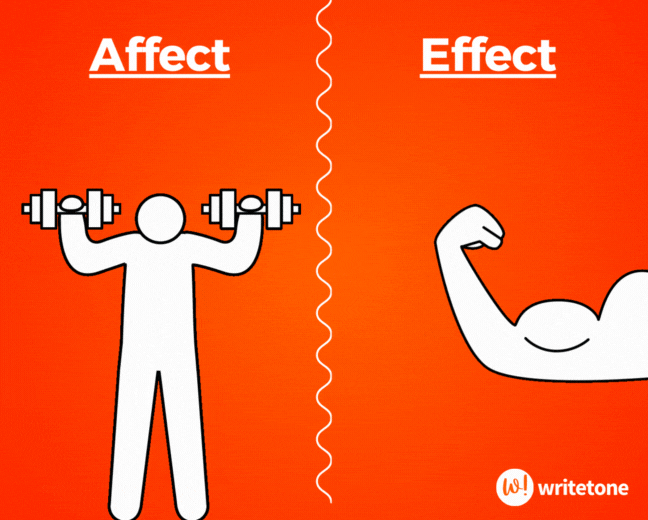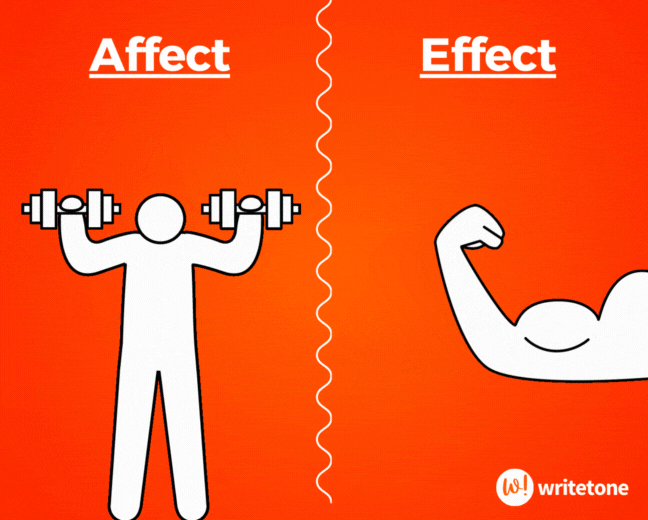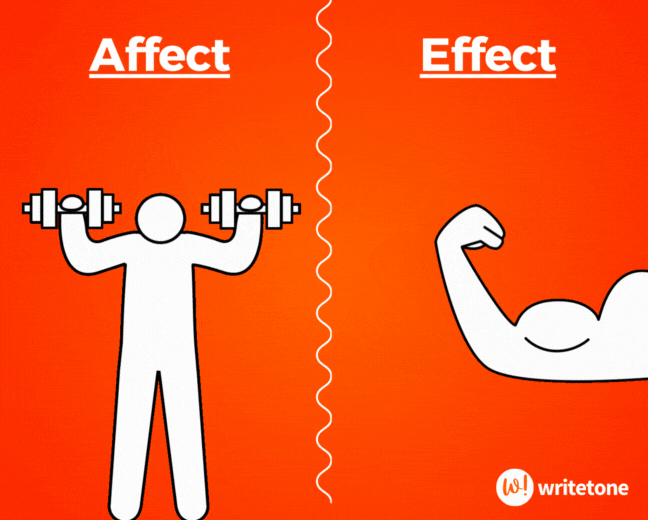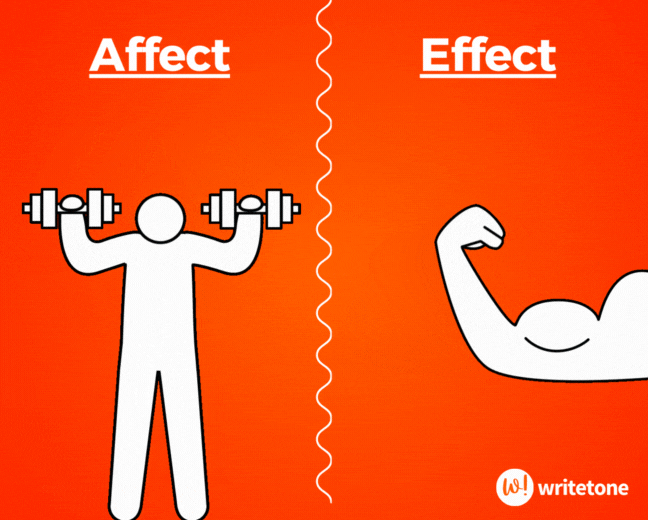
Affect (v) means to influence or have an impact on something. Effect (n) is the result or consequence of something.
For Example:
The teacher hoped the new teaching method would affect the students positively, and indeed, it had a significant effect on their engagement.
Accept vs. Except
Accept (v) means to receive or agree to something.
Except (v) means to exclude or leave out.
For Example:
She decided to accept all the job offers except the one from the company she didn't like.
Apart vs. a part
Apart (adj) means separated, not together.
A part (n) means one piece of a larger set.
For Example:
Living apart from her family, she felt like a part of a larger community in the city.
Assure vs. Ensure vs. Insure
Assure (v) means to convince, guarantee, or confirm.
Ensure (v) means to make sure (by action)
Insure (v) means to take out an insurance policy.
For Example:
The company wanted to assure its employees of job security, so they took steps to ensure their well-being and insured them against unforeseen circumstances.
Breath vs. Breathe
Breath (n) means air that a person inhales and exhales.
Breathe (v) means to inhale and exhale air.
For Example:
My doctor told me to breathe in, so I took a deep breath
Complement vs. Compliment
Complement (v) means to complete or enhance something.
Compliment (v) means to express praise or admiration.
For Example:
This scarf can complement an outfit and you will receive a nice compliment on your attire.
Compose vs. Comprise
Compose (v) means to create or write something.
Comprise (v) means to consist of or make up something.
For Example:
The orchestra will compose a beautiful piece that will comprise various musical elements.
| Never make a grammatical mistake again.
Conscious vs. Conscience
Conscious (adj) means aware. Conscience (n) means inner voice or sense of right and wrong.
For Example:
Though she was conscious of her actions, her conscience urged her to reconsider.
Desert vs. Dessert
Desert (n / v) is a barren wasteland. Dessert (n) is a sweet dish served after a
For Example:
After exploring the desert, they indulged in a delicious dessert.
Discrete vs. Discreet
Discrete (adj) means separate or distinct. Discreet (adj) means showing good judgment or prudence.
For Example:
The discrete sections of the report were presented with discreet attention to confidentiality.
Farther vs. Further
Farther (adj / adv) relates to physical distance.
Further (adj / adv) Further means metaphorical distance or advancement.
For Example:
The camp side is farther from her house than she thought, but she decided to explore it further.
Its vs. It's

Its (pr) is a possessive pronoun that shows ownership.
It's (c) is a contraction of it is or it has.
For Example:
The dog waggedits tail, showing it's in a good mood.
Lay vs. Lie
Lay (v) means to place a being or an object on a surface.
Lie (v) means to lay oneself on a surface.
For Example:
The cat refused to lie down, so she decided to lay a soft blanket for it.
Lead vs. Led
Lead (n / v) can be a noun meaning a guiding person or a verb meaning to guide or direct.
Led (v) is the past tense of the verb to lead.
For Example:
John will lead the group as he had led a larger group in the past.
Lose vs. Loose
Lose (v) means to fail to keep or fail to win.
Loose (adj) describes something that is not tight or not well attached.
For Example:
If you don't tighten the screws, you mightlose the loose parts of the furniture.
Passed vs. Past
Passed (v) is past tense of the verb to pass. Past (prep / adj) means beyond or gone by in time.
For Example:
As she passed by the old house, memories of the past flooded her mind.
Pore vs. Pour
Pore (v) means to look carefully.
Pour (v) means to dispense liquid from a container.
For Example:
She decided to pore over the details of the contract before she would pour herself a cup of coffee.
Stationary vs. Stationery

Stationary (adj) means not moving.
Stationery (n) refers to writing materials.
For Example:
The car remained stationary at the traffic light while she wrote a note on her new stationery.
Statue vs. Statute
statue (n) means a 3D artistic form, such as a sculpture, made to look like a person or object.
statute (n) means a law.
For Example:
After exploring the desert, they indulged in a delicious dessert.
Desert vs. Dessert
Desert (n / v) is a barren wasteland. Dessert (n) is a sweet dish served after a
For Example:
The statue in the park depicted a historical figure, while the statute nearby outlined the city's noise regulations.
There vs. Their vs. They're

There (adv) indicates a place or position.
Their (pr) is a possessive pronoun that shows ownership.
They're (c) is a contraction of they are.
For Example:
They're planning to visit their favourite park tomorrow, and I heard there will be a special event.
To vs. Too vs. Two
To (prep) indicates direction, purpose, or degree.
Too (adv) means excessively or also.
Two is a number.
For Example:
She wanted to invite two friends to the party, but they were too busy with their jobs.
Then vs. Than
Then (adv) indicates a sequence of time.
Than (c) is used in comparisons.
For Example:
I would rather finish my work now than procrastinate and deal with it later; then, I can enjoy a relaxing evening
Where vs. Were
Where (adv) indicates a place or position.
Were (v) is the past tense of the verb to be.
For Example:
They were at the place where she told them to meet.
Whose vs. Who's
Whose (pr) shows ownership.
Who's (c) is a contraction of who is or who has.
For Example:
Who's going to check whose answers to ensure accuracy?
Your vs. You're

Your (pr) is a possessive pronoun that shows ownership.
You're (c) is a contraction of "you are."
For Example:
You're responsible for submitting your report by the end of the day.
How Writetone Can help ?
| Try Writetone for free now!

Writetone is an AI-powered writing tool that can help you avoid common writing mistakes. It has a variety of features, including a grammar checker, a paraphrasing tool, and a summarizer. Writetone can also help you improve your tone and make your writing more concise and impactful. With Writetone, you can be confident that your writing is clear, accurate, and effective.
Conclusion
The English language has a lot of words that sound or look similar but have different meanings. This can be hard to understand, especially if you want to express your thoughts clearly. Use Writetone, an AI-powered writing tool that can help you understand the nuances of commonly confused words.